Herbicides for control of clethodim-resistant annual ryegrass
Author: Christopher Preston, Peter Boutsalis, Samuel Kleemann, Rupinder Saini and Gurjeet Gill, School of Agriculture, Food and Wine, Adelaide University | Date: 17 Feb 2015
ɸExtra technical comment by Protech Consulting Pty Ltd
GRDC project code: UA00144, UCS00020
Take home messages
- Pre-emergent herbicides alone are insufficient to effectively manage annual ryegrass in break crops.
- Increased competition provided by hybrid canola varieties will improve the performance of pre-emergent herbicides.
- Crop topping in canola offers an opportunity to reduce annual ryegrass seed set.
Managing clethodim resistance in annual ryegrass
Weed surveys across the southern region are showing alarming levels of resistance to clethodim in annual ryegrass. Clethodim is the last Group A herbicide that provides effective control of herbicide resistant annual ryegrass. It has become an exceptionally important herbicide in annual ryegrass weed management strategies. The loss of clethodim to resistance will make annual ryegrass management more difficult. In order to address this problem, we have been looking at alternative herbicide strategies to clethodim in break crops.
In faba beans, sole reliance on pre-emergent herbicides failed to adequately manage annual ryegrass and large yield penalties occurred (Table 1). This trial was conducted in 2014 on a clethodim resistant population at Roseworthy, SA. Clethodim at 500 mL/ha following a pre-emergent application of simazine suppressed the ryegrass and the dry spring in 2014 ensured the ryegrass plants had few heads. However, the effect of the early ryegrass competition on yield was obvious. Addition of Factor® to clethodim in 2014 reduced ryegrass numbers further and protected yield. This remains the most effective currently registered option for faba beans. Environmental conditions in 2014 of high rainfall early in the season likely favoured simazine activity.
Table 1. Ryegrass plant numbers, seed heads and faba bean grain yield at Roseworthy, SA in 2014 following a variety of treatments to control clethodim resistant annual ryegrass.
|
Treatment |
Ryegrass plants |
Ryegrass seed heads |
Grain yield |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Simazine (1.5 kg/haa) Pre + Clethodim (500 mL/ha) Post |
112bc |
8a |
2.11a |
|
Simazine (1.5 kg/haa) Pre + Clethodim (500 mL/ha) + Factor (180 g/ha) Post |
22a |
2a |
2.40c |
|
Product A Pre |
185bcd |
281bc |
2.17ab |
|
Product B Pre |
208bcd |
219b |
2.19abc |
|
Product B + Avadex® Xtrab (1.6 L/ha) Pre |
199bcd |
252bc |
2.19abc |
|
Boxer Gold® (2.5 L/ha) Pre |
325d |
449c |
2.16ab |
|
Boxer Gold® (2.5 L/ha) + Avadex® Xtrab (1.6 L/ha) Pre |
221cd |
287bc |
2.06a |
|
Product C Pre |
101b |
256bc |
2.35bc |
Values with different letters within a column are significantly different (p = 0.05)
ɸ a The rate on the Gesatop Granules label is 1.0-1.4 kg/ha and on the Gesatop Granules WG label is 1.1-1.4 kg/ha
ɸ b Not registered for annual ryegrass in faba beans; but registered for wild oats in faba beans (and at this rate)
In TT canola in 2014, clethodim was not as effective at controlling annual ryegrass as it was in faba beans, probably due to lower early competitiveness of the TT canola (Table 2). Rustler® was the best of the stand-alone pre-emergent herbicide options examined, although weeds that emerged through this treatment were highly competitive and reduced yield. Addition of clethodim to Rustler® tended to stunt these weeds and reduce their competitiveness. The reduced rate of Factor® that can be used in canola, compared with pulse crops makes this product less effective on annual ryegrass that has low levels of resistance to this herbicide.
Hybrid canola varieties offer greater competition than TT open pollinated varieties. This can help limit seed production from surviving ryegrass plants (Table 3). In the Roseworthy trial we compared TT canola (ATR Stingray) with a Clearfield hybrid (45Y82). However, annual ryegrass has widespread resistance to the imidazolinone herbicides and this was present at the site, as was some resistance to trifluralin. This limited the options available for control of annual ryegrass in Clearfield canola. Pre-emergent herbicides performed better in the hybrid canola than in the open pollinated canola due to the increased competition provided by the Clearfield hybrid. Rustler pre-emergent with clethodim post-emergent was one of the better treatments despite resistance to clethodim being present.
Table 2. Ryegrass plant numbers, seed production and TT Canola grain yield at Roseworthy, SA in 2014 following a variety of treatments to control clethodim resistant annual ryegrass.
|
Treatment |
Ryegrass plants |
Ryegrass seed |
Grain yield |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Atrazineɸ (1.5 kg/ha) Pre + Clethodim (500 mL/ha) Post |
522ab |
6785a |
1.69abc |
|
Atrazine (1.5 kg/ha) Pre + Clethodim (500 mL/ha) + Atrazine (1 kg/ha) Post |
361a |
2956a |
1.88a |
|
Atrazine (1.5 kg/ha) Pre + Clethodim (500 mL/ha) + Factor (80 g/ha) Post |
282a |
3274a |
1.84ab |
|
Product A Pre |
864b |
51743cd |
1.15de |
|
Rustler (1 L/ha) Pre |
354a |
32781bc |
1.49cd |
|
Rustler® (1 L/ha) Pre + Clethodim (500 mL/ha) Post |
324a |
13396ab |
1.74abc |
|
Atrazineɸ (1.5 kg/ha) Pre + Product D Post |
876b |
63124d |
1.00de |
|
Atrazineɸ (1.5 kg/ha) Pre + Product E Post |
308a |
10996a |
1.61bc |
|
Product E Pre |
869b |
51192cd |
1.26d |
Values with different letters within a column are significantly different (p = 0.05)
ɸ Pre emergence registered for suppression only (1.1 – 2.2 kg/ha). Post emergence registered for control of 1-2 leaf stage only (0.5 – 1.1 kg/ha)
Table 3. Ryegrass plant numbers, seed production and Clearfield Canola grain yield at Roseworthy, SA in 2014 following a variety of treatments to control clethodim resistant annual ryegrass.
|
Treatment |
Ryegrass plants |
Ryegrass seed |
Grain yield |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Trifluralin (2 L/ha) + Avadex® Xtra Pre + Intervix® (750 mL/ha) + Clethodim (500 mL/ha) Post |
632ab |
5404a |
1.71abc |
|
Trifluralin (2 L/ha) + Avadex® Xtra Pre + Intervix® (750 mL/ha) + Clethodim (500 mL/ha) + Factor (80 g/ha) Post |
128a |
7915a |
1.79a |
|
Product A Pre |
1697d |
45347d |
1.41bcd |
|
Rustler® (1 L/ha) Pre |
553ab |
17270ab |
1.65abcd |
|
Rustler® (1 L/ha) Pre + Clethodim (500 mL/ha) Post |
385ab |
3663a |
1.84a |
|
Trifluralin (2 L/ha) Pre + Product D Post |
1206cd |
33299cd |
1.44bcd |
|
Trifluralin (2 L/ha) Pre + Product E Post |
589ab |
28159bc |
1.61abcd |
|
Product E Pre |
1643d |
27107bc |
1.36d |
Values with different letters within a column are significantly different (p = 0.05).
In 2015, RT canola (canola with tolerance to both glyphosate and triazine herbicides) will be commercially available. We are examining the potential for RT canola to be used as part of a strategy to control clethodim resistant annual ryegrass in high rainfall areas with trials at Lake Bolac and west of Minimay in Victoria. The strategy is comparing a TT option with an option including both glyphosate and triazines and a third option including crop topping.
As the population at the Neuarpurr site is resistant to clethodim, the TT strategy was the least effective option (Figure 1). Substituting Roundup Ready herbicide for clethodim reduced ryegrass numbers. Crop topping should have an additional effect on seed set. The trial will be sown to wheat in 2015 with several strategies used in an attempt to maximise the reduction in annual ryegrass populations.
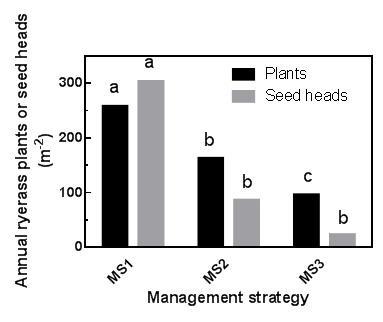
Figure 1. Annual ryegrass plant numbers and seed heads following three management strategies in RT canola at Neuarpurr, Vic. MS1 = simazine pre, clethodim + atrazine post; MS2 = simazine pre, Roundup Ready herbicide post, Roundup Ready herbicide plus atrazine post; MS3 = Rustler® plus Avadex® Xtra pre, Roundup Ready herbicide post, Roundup Ready herbicide plus atrazine post, Weedmaster® DST crop top. Bars with different letters for each measurement are significantly different (p = 0.05).
Crop topping canola
Late in 2014, Weedmaster® DST was registered for use as a crop-topping application in canola. This provides an opportunity to control grass weed seed set in canola crops. The registered uses are to apply over the top of the crop from 20% canola seed colour change or under the windrower. To use Weedmaster® DST effectively for crop topping the correct timing, rate of herbicide, water volume and environmental conditions need to be followed.
The main problem with over the top use is to get the herbicide through the canola canopy and onto the ryegrass growing underneath. Higher water rates and coarse spray quality will help achieve this. For under the windrow applications, water rates will always be low. In addition, windrowing may be done when environmental conditions are less favourable for glyphosate to work. Increasing the rate of Weedmaster® DST may help overcome these issues (Figure 2). Ryegrass maturity can also have an impact when crop topping canola. Seed set will not be controlled on annual ryegrass that has matured at the time of windrowing.
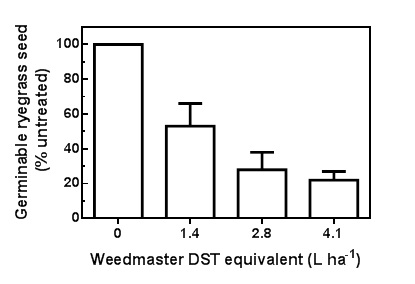
Figure 2. Germination of annual ryegrass seed following application of glyphosate at windrowing in canola. Average of two trials in mid-north of SA in 2010.
Contact details
Christopher PrestonSchool of Agriculture, Food & Wine, University of Adelaide PMB1 Glen Osmond SA 5064
(08) 8313 7237
christopher.preston@adelaide.edu.au
Was this page helpful?
YOUR FEEDBACK
